lvef 40 percent An ejection fraction below 40 percent is classified as heart failure with a reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). It occurs when one of your heart’s chambers isn’t able to contract properly.
Citi pakalpojumi: Viesnīca, privātā zona ( VIP), sertificēta fizioterapeite, sporta treneri, fitnesa zāle, ūdens airobika, Aqua Zumba, ūdens SPA procedūras. Pievienot favorītiem. Kontakti. +371 26825940.
[email protected]. Kurzemes iela 8, Jēkabpils. Mājaslapa. Facebook. Instagram. Darba laiks. Pirmdiena 11:00-21:00. Otrdiena 11:00-21:00.
0 · what is lvef in cardiology
1 · lvef survival rate
2 · lvef 40 treatment
3 · lvef 35 40 meaning
4 · high left ventricular ejection impedance
5 · ejection fraction heart failure chart
6 · ejection fraction by age chart
7 · 40% lvef meaning
Ar pilniem loterijas noteikumiem aicinām iepazīties mājas lapā www.cipsi.lv. Atļaujas Nr. 5074. Skatīt loterijas noteikumus. Loterijas periods 2. jūlijs, 2018 - 31. augusts, 2018. LoterijasPiedalies un laimē vērtīgas balvas jau šodien. Balvas 48 Atrodi loterijas pēc visinteresantākajām balvām.
Ejection fraction (EF) is a measurement, expressed as a percentage, of how much blood the left ventricle pumps out with each contraction. An ejection fraction of 60 percent means that 60 percent of the total amount of blood in the left ventricle is pushed out with each heartbeat. A normal heart’s ejection . See more
An EF from 41 to 49 percent might be considered too low. It does not always indicate that a person is developing heart failure, but it could indicate damage, perhaps from a previous heart attack. An ejection fraction measurement under 40 percent might be . See moreYour health care professional might recommend one or more of these tests to measure your ejection fraction: 1. Echocardiogram(or “echo”) - the most widely used test 2. . See moreYour health care professional might mention one of these two EF-related scenarios: 1. Preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF)– also . See more
40% to 49% is mid-range ejection fraction: The heart’s pumping ability is slightly below normal. You might not experience heart failure symptoms. Or, you may have symptoms with physical .
An ejection fraction below 40 percent is classified as heart failure with a reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). It occurs when one of your heart’s chambers isn’t able to contract properly. Ejection fraction is measured as a percentage of the total amount of blood in your heart that is pumped out with each heartbeat. A normal ejection fraction is 50 percent or higher. An ejection fraction below 40 percent means . LVEF is the fraction of chamber volume ejected in systole (stroke volume) in relation to the volume of the blood in the ventricle at the end of diastole (end-diastolic volume). Stroke volume (SV) is calculated as the difference .
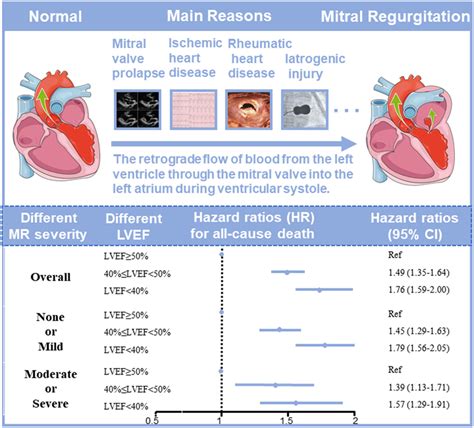
If you have been prescribed medications for heart failure, diabetes, high blood pressure or another underlying cause, taking your prescribed medication may also improve your ejection fraction. Over time, as the . Inflection points were at an LVEF of 50% for cardiovascular death, 40% for pump failure death, 35% for heart failure hospitalization, and no inflection point for sudden death. A strength of this study is the use of multiple clinical .
For an ejection fraction in the range of 50% to 55%, most of the commonly used tests, if carefully performed, are accurate within a few percentage points (e.g. 55% plus or minus 3%). With respect to the lower .
A normal ejection fraction of 55 to 65% is considered a sign of a healthy heart. People with an ejection fraction lower than 50% might be suffering from systolic heart failure. This is also termed Heart Failure with reduced ejection fraction. A reduced LV ejection fraction is usually 40% or less. Even if you have a normal ejection fraction, your overall heart function may not be healthy. Talk with your health care provider if you have concerns about your heart. Some things that may cause a reduced ejection fraction are: Weakness of the heart muscle, such as cardiomyopathy. Heart failure (HF) with mildly reduced ejection fraction (EF) (HFmrEF) has been extensively studied, generally using an EF of 40–49%, and accounts for up to 25% of patients with HF. LVEF is calculated from: LVEF: [SV/EDV] x 100 Normal ranges for two-dimensional echocardiography obtained LVEF as per the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging are: LVEF (%) among the male population: 52% to 72% normal range. 41% to 51 mildly abnormal. 30% to 40% moderately .
As the percentage falls, it tells the doctor that the heart failure is getting worse. In general, if the EF falls below 30%, it's relatively severe. A reading of 20% or below is very severe heart .
what is lvef in cardiology
Ejection fraction measures the percentage of blood that is pumped out by the left ventricle each time the heart . but it may be a sign of heart damage or a prior heart attack. An ejection fraction rate of 40% or lower may indicate heart failure or cardiomyopathy. . LVEF Mortality ≤15% 51% 16–25% 41.7% 26–35% 31.4% 35–45% .
Inflection points were at an LVEF of 50% for cardiovascular death, 40% for pump failure death, 35% for heart failure hospitalization, and no inflection point for sudden death. A strength of this study is the use of multiple clinical trials of patients with heart failure across the LVEF spectrum. This allowed detailed clinical data on each .The ejection fraction is one of the most common parameters used to diagnose heart failure. It refers to the percentage of blood the left ventricle pumps out during the systolic phase. Normal Ejection Fraction by Age is 55 to 65%. An EF from 41 to 49 percent might be considered too low. It does not always indicate that a person is developing heart failure, but it could indicate damage, perhaps from a previous heart attack. An ejection fraction measurement under 40 percent might be evidence of heart failure or cardiomyopathy. In severe cases, EF can be even lower than 40.
The normal percentage of blood ejected from the heart is in the range of 50-70% depending on different factors. If the left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is 45% (& that is not a measurement error), then it is mildly reduced. The list of possible reasons why is quite extensive & should be discussed with your doctor.
• In the CHARM-Preserved trial, 3023 patients with symptomatic HF (nearly all NYHA class II or III) and an LVEF >40 percent and controlled blood pressure were randomly assigned to either candesartan (mean dose at six months: 25 mg) or placebo . The mean LVEF was 54 percent. At a median follow-up of 37 months, there was a small but uncertain . The heart failure life expectancy calculator is a simple, yet effective, tool for predicting the 1-year and 3-year survival odds of someone with congestive heart failure.. In the article below, we will focus on congestive heart failure/CHF prognosis, the estimates on how long can you live with congestive heart failure, and the average CHF life expectancy for a given . Digoxin reduced HF hospitalization to a greater extent in those with lower LVEF. The HR for digoxin versus placebo was 0.71 (95% CI: 0.65 to 0.77) in those with LVEF of <40%, 0.80 (95% CI: 0.63 to 1.03) in those with LVEF of 40% to 49%, and 0.85 (95% CI: 0.62 to 1.17) in those with LVEF of ≥50%. Angiotensin receptor–neprilysin inhibitors For an ejection fraction in the range of 50% to 55%, most of the commonly used tests, if carefully performed, are accurate within a few percentage points (e.g. 55% plus or minus 3%). With respect to the lower limit of “normal” LVEF, it is important to remember that even at rest, the LV pumps a slightly different amount of blood in every beat.
Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) has been a key variable for the diagnosis and management of heart failure over the last three decades. The British Society of Echocardiography recently updated their normal reference intervals for assessment of cardiac dimensions and function.1 They describe four categories of left ventricular function and a ‘normal’ LVEF is . The average left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) in the study participants was 57%. It is indicated for symptomatic HFrEF, HFmrEF, and HFpEF. . (ICM) at least 40 days post-MI on chronic goal-directed medical . Background: The left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) guides treatment of heart failure, yet this data has not been systematically collected in large data sets. We sought to characterize the epidemiology of incident heart .
We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. It scans the heart and takes measurements to find out what percentage of your blood is being pumped out with each heartbeat. . Most people with Stage B have an ejection fraction of 40% or less . In a trial that included 626 patients with an LVEF ≥40 percent and a pulmonary capillary wedge pressure ≥25 mmHg during exercise, patients were randomly assigned to placement of an interatrial shunt device or to a sham procedure . After 24 months of observation, the rates of death (1 percent in both groups), stroke (1 versus 0 events in the . lar outcomes increased with decreasing LVEF, although there were different LVEF thresholds for different out-comes. Inflection points were at an LVEF of 50% for cardiovascular death, 40% for pump failure death, 35% for heart failure hospitalization, and no inflection point for sudden death. A strength of this study is the use of multiple clini-
This means that 50–70 percent of the total volume of blood in the left ventricle is pumped out each time the heart beats. An ejection fraction of 40 percent or less might be evidence of heart . Indeed, the prevalence of peripheral edema was somewhat higher in patients with a LVEF >60% (48% versus 40% in people with a LVEF >40% to 50%) despite an identical rate of diuretic treatment and similar kidney function. However, the difference in NT-proBNP between the 2 LVEF groups was striking. A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes. It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as I50.1.A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition.reduced LVEF [≤40%] (HFrEF)] A chronically low ejection fraction less than 30% is an important threshold in qualification for disability benefits in the US. [22] . ratio, or percentage, whereas the stroke volume, end-diastolic volume or end-systolic volume are absolute measurements. [citation needed] History
Guidelines for the management of patients with heart failure (HF) use subtypes based on cutoffs of LVEF: reduced LVEF (HFrEF, LVEF ; 40%), mid-range LVEF (HFmrEF, 40-50%), and preserved LVEF (HFpEF, LVEF >50%). However, LVEF is not static, and therapies might not be optimally determined solely based on LVEF.We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. On the other hand, left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is the percentage of oxygen-rich blood pumped out from the left ventricle into the arteries that carry blood to vital organs, muscles, and tissues. Typically, doctors use the term “ejection fraction” when they refer to LVEF. If your heart is healthy and well functioning, the .
lvef survival rate
Product details. Gifting. LV Stellar Scarf. Call for inquiry. Women. Accessories. Scarves. LV Stellar Scarf. LOUIS VUITTON Official International site - LV Stellar Scarf S00 is exclusively on louisvuitton.com and in Louis Vuitton Stores. Discover more of our Accessories Scarves Collection by Louis Vuitton.Svinot “CITRO” 4. gadu jubileju, sveicam šī gada 8.novembra jaundzimušos. Uzzini vairāk. Lasīt visas ziņas.
lvef 40 percent|what is lvef in cardiology