difference between biological and technical replicates The basic definitions of technical and biological replicates are as follows: Technical replicates: a test performed on the same sample multiple times; i.e., if there . Past meets present: inside 30 Avenue Montaigne, Dior’s new look Parisian flagship. The spiritual home of Dior, global flagship 30 Avenue Montaigne in Paris reopens its doors with a new look, a museum, a restaurant and an apartment for overnight stays. Left, men’s ready-to-wear toiles on display.
0 · technical and biological replicates meaning
1 · replication vs pseudoreplication
2 · replicate vs duplicate experiments
3 · pseudoreplication vs genuine replication
4 · how to avoid pseudoreplication
5 · biological replication vs pseudoreplication
6 · biological replication and pseudoreplication
7 · biological replicates vs technical
WOW LIST. 30 Avenue Montaigne: 2023 Works of Wonders. Christian Dior’s iconic Right Bank hôtel particulier was updated by architect Peter Marino. .
When it comes to quantification, biological and technical replicates are key to generating accurate, reliable results. While they both offer researchers valuable data, each answers distinct questions about data .
lv portemonnaie damen
For biological studies, there are two main types of replicates: biological and technical. Things to do before submitting. To avoid delays closer to publication and help reviewers to. Biological replicates are parallel measurements of biologically distinct samples that capture random biological variation, which may itself be a subject of study or a noise .• Biological replicates are parallel measurements of biologically distinct samples that capture random biological variation, which may itself be a subject of study or a source of noise. • .
The basic definitions of technical and biological replicates are as follows: Technical replicates: a test performed on the same sample multiple times; i.e., if there .There are two primary types of replicates: technical and biological. Technical replicates involve taking one sample from the same source tube, and analyzing it across multiple .• Biological replicates are parallel measurements of biologically distinct samples that capture random biological variation, which may itself be a subject of study or a source of noise. • .
This Focus tackles the issue of technical versus biological replicates, what constitutes appropriate biological replicates, and appropriate statistical analysis for data with small sample sizes.
Technical replicates: repeated measurements of the same sample that represent independent measures of the random noise associated with protocols or equipment. Technical replicates .
Scientists use replicates in their experiments to do statistics. But why are replicates useful and what is the difference between a biological and a technical replicate? .
A biological replicate is an individual of the same group in an experiment. For example, we want to test of drought on Pinus sylvestris. We need two groups of samples, Control and Drought, and .technical replicates as biological is misleading. When performing in vitro cell culture analysis, please note that different wells on the same plate, cultured and run together in an assay, do not . Congratulations! You now have a solid understanding of the difference between technical and biological replicates. Technical replicates involve repeating the same experiment on the same individual or sample, .
Here, we discuss the issue of reproducibility at the level of individual experiments. First, it is important to distinguish between technical and biological replicates. Technical replicates tell something about the reproducibility of an assay, not the reproducibility of the phenomenon under study. Generally, biological replicates are defined as measurements of biologically distinct samples that show biological variation (21). In contrast, technical replicates are repeated measurements of the same sample that show independent measures of the noise associated with the equipment and the protocols.
Treating technical replicates as biological replicates is called pseudoreplication and often produces low estimates of variance and erroneous test results. The difference between technical and biological replicates depends on how one defines the population of interest. For example, measurements on cells within one culture flask are considered .However, technical replicates add cost and reduce the throughput, so you must decide on an optimal number of technical replicates, balancing benefits vs. costs. In basic research, triplicates are a commonly selected replicate number. Biological replicates are different samples that belong to the same group. They are amplifications that use the .%PDF-1.6 %âãÏÓ 194 0 obj >stream hÞ´ ÝjÂ@ F_eîL 6»IýAD°¦¥Ò*¢ ^Ô^l6£N ³2n(éÓwcEô {1³Ì~sÎöz `8 Ç•Ý öVz÷ ö'€T±‚µ7Ÿ>‡óé . Finally, we discuss a clinical situation where distinguishing between biological vs. technical replicates can lead to absurd situations in clinical decision makings. We conclude that discrimination between biological vs. technical replicates is helpful in experimental studies but is difficult to implement in everyday's clinical practice.
The wrong choice of replicate cannot be fixed by a clever statistical analysis after the experiment is completed (e.g., using multilevel or hierarchical models); it needs to be planned at the design stage. . we argue that the frequent and common distinction made between ‘biological’ and ‘technical’ replication is unhelpful because .
Now a technical sample is, in this case, simply the sample split after the two different procedures, so you have 3 technical replicates of A and 3 technical replicates of B.
technical and biological replicates meaning
In cell biology In whole organism (e.g. mouse) work, the difference between technical replicates and biological replicates is pretty obvious – technical replicates are readings derived from a single mouse, biological replicates are readings derived from different mice. In cell biology it can be a bit harder to define things. The Bland-Altman plot of the natural log-transformed data for the technical replicates of D. simulans biological replicate 3 (Figure 5, and Additional file 11) clearly shows that at lower levels of expression there is larger disagreement between technical replicates. However, although the absolute disagreement is a function of abundance, the . Hence, you measure technical replicates on the same day. Biological variance is introduced by prolonged culturing (react to differences of FCS, culture flasks, Selection by splitting, etc.). To display biological variance, you measure at different timepoints and minimize technical variance by taking the mean of tech replicates.
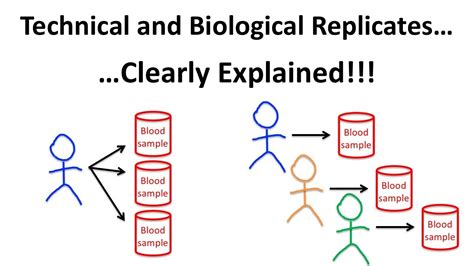
Generally, biological replicates are defined as measurements of biologically distinct samples that show biological variation (21). In contrast, technical replicates are repeated measurements of the same sample that show independent measures of the noise associated with the equipment and the protocols. A, Diagrammatic illustration summarizing the traditional definition of technical and biological replicates commonly adopted in biological studies. B, Diagrammatic illustration depicting the different experimental designs available . Scientists use replicates in their experiments to do statistics. But why are replicates useful and what is the difference between a biological and a technica.• Biological replicates are parallel measurements of biologically distinct samples that capture random biological variation, which may itself be a subject of study or a source of noise. • Technical replicates are repeated measurements of the same sample that represent
To differentiate between technical and biological replicates, a useful question to ask is whether or not the follow-up test should give, in expectation, exactly the same quantitative result as the original study. Technical replication tests do not introduce independency into the experimental system and can mainly be applied to measure errors in .
The mixed effects model analysis for measurement B results in “not-at-all-close-to-significant” differences between groups; no real surprise. What does this example teach us? Averaging technical replicates (as in the left panel) and running statistical analyses on average values means losing potentially important information. The most challenging and least considered aspect of many experiments is the appropriate selection of a randomized set of individual samples (i.e., biological replicates) per biological group (i.e., treatment/experimental conditions) while minimizing their inherent variability [13].Both the transcriptome and proteome are highly sensitive to the inherent .
Accounts for the Differences Between Biological and Technical Replicates. A higher degree of similarity is expected between technical replicates compared to biological replicates, where the differences between biological replicates represent true biological variability while the differences between technical replicates are predominantly artifactual bindings or signal noise.Biological replicates are required if inference on the population is to be made, with three biological replicates being the minimum for any inferential analysis. Desired statistical power, that is the capacity for detecting statistically significant differences in gene expression between experimental groups.
Download scientific diagram | Elucidation of differences between technical and biological replicates from publication: Data Mining and Meta-Analysis on DNA Microarray Data | Microarray technology . Is there one "right" way to display the data? Is there an alternative that shows the variation both among technical replicates and among biological replicates? *biological replicates: measurements of distinct biological samples, e.g. three different animals to assess biological variation. technical replicates: repeated measurements of the same .
Combine each technical replicates for each biological replicate, then combine each biological replicate into a group (i.e. treated group or baseline group). . What is the difference between a replicate and an experimental unit? These three are terms used when multiple samples are taken from a single experimental unit. Replicate: A replicate .
replication vs pseudoreplication
30 Montaigne. The Dior 30 Montaigne bag is a House icon made from the finest .
difference between biological and technical replicates|biological replicates vs technical