lvef 60-65 Your health care professional might mention one of these two EF-related scenarios: 1. Preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF)– also referred to as diastolic heart . See more $5,899.00
0 · what is lvef in echocardiogram
1 · what does 60% mean
2 · lvef spect nuclear stress viability
3 · left ventricular ejection impedance meaning
4 · left ventricular ejection fraction lvef
5 · high left ventricular ejection impedance
6 · heart pumping capacity by age
7 · borderline left ventricular ejection fraction
Rimless Sunglasses: These glasses are synonymous with the 2000s. Their unique shapes and colorful lenses can add a playful touch to your look. Shield Sunglasses: These sunglasses are characterized by a single large lens that covers both eyes, offering a futuristic feel. Choosing the Right Y2K Sunglasses
Ejection fraction (EF) is a measurement, expressed as a percentage, of how much blood the left ventricle pumps out with each contraction. An ejection fraction of 60 percent means that 60 percent of the total amount of blood in the left ventricle is pushed out with each heartbeat. A normal heart’s ejection . See moreAn EF from 41 to 49 percent might be considered too low. It does not always indicate that a person is developing heart failure, but it could indicate damage, . See more
Your health care professional might mention one of these two EF-related scenarios: 1. Preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF)– also referred to as diastolic heart . See moreYour health care professional might recommend one or more of these tests to measure your ejection fraction: 1. Echocardiogram(or “echo”) - the most widely used . See moreLeft ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) Ejection fraction typically refers to the left side of the heart. It shows how much oxygen-rich blood is pumped out of the left ventricle to most of the body’s . Ejection fraction is a measurement doctors can use to help diagnose heart failure. A normal range is between 52% and 72% for males .
A left ventricle (LV) ejection fraction of about 50% to 70% is categorized as normal. A mildly reduced LV ejection fraction is usually between 41% and 49%. A reduced LV ejection . Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) 1 has persisted as the primary measure of left ventricular systolic function despite flaws in this approach. Patients with heart failure are relieved when the LVEF is reported . Even accepting this general range, there will be a few people with no recognizable heart problem who have an LVEF in the high 40s and many more with clear-cut heart problems who have an LVEF in the high 50s or even .
An ejection fraction of 60 percent means that 60 percent of the total amount of blood in the left ventricle is pushed out with each heartbeat. A normal heart’s ejection fraction is between 55 and 70 percent. This indication . Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is the central measure of left ventricular systolic function. LVEF is the fraction of chamber volume ejected in systole (stroke volume) in relation to the volume of the blood in the ventricle at . increased risk of death with an LVEF >65% for both those with and without heart failure. One potential reason for the different results is that clinical trials (combined for the .
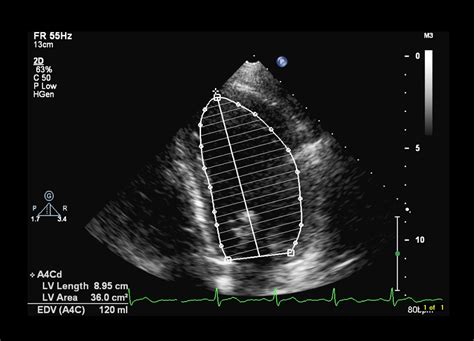
what is lvef in echocardiogram
The current ACCF/AHA guidelines classify patients with a left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of ≥50% as having a preserved ejection fraction (4), and previous studies have found that . A healthy heart contracts (empties blood) and relaxes (refills blood) 60-80 times each minute. With each heartbeat, the heart pumps blood from the left and right ventricle. In most cases, ejection fraction refers to the percentage .
Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) has been a key variable for the diagnosis and management of heart failure over the last three decades. The British Society of Echocardiography recently updated their normal reference intervals for .
The research is important given the recent yet unexplained finding of excess mortality in subjects with LVEF deviated from 60 to 65% in the general population. 10 Our results are relevant. The findings provide critical evidence for clinical risk evaluation and management. Furthermore, our study has crucial implications for the LVEF threshold .
Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is the central measure of left ventricular systolic function. LVEF is the fraction of chamber volume ejected in systole (stroke volume) in relation to the volume of the blood in the ventricle at the end of diastole (end-diastolic volume). Stroke volume (SV) is calculated as the difference between end-diastolic volume (EDV) and .
The ejection fraction (EF) is the amount of blood your heart pumps (or ejects) with each heartbeat and is a useful way of measuring LVSD. A normal EF is about 55-65 per cent. It’s important to understand that “normal” is not 100 per cent. Measuring the EF helps your doctor to understand how well the heart is pumping. Overall, adjusted hazard ratios (HR) for mortality showed a u-shaped relationship for LVEF with a nadir of risk at an LVEF of 60–65%, a HR of 1.71 [95% confidence interval (CI) 1.64–1.77] when ≥70% and a HR of 1.73 (95% CI 1.66–1.80) at LVEF of 35–40%. Similar relationships with a nadir at 60–65% were observed in the validation . eft ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF)1 has per-sisted as the primary measure of left ventricular systolic function despite flaws in this approach. Patients with heart failure are relieved when the LVEF is reported as normal, and clinicians may use the report of a depressed LVEF to persuade patients of the need for treatment.
Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is the central measure of left ventricular systolic function. LVEF is the fraction of chamber volume ejected in systole (stroke volume) in relation to the volume of the blood in the ventricle at the end of diastole (end-diastolic volume). Stroke volume (SV) . Ejection fraction (EF) is a measurement, expressed as a percentage, of how much blood the left ventricle pumps out with each contraction. An ejection fraction of 60 percent means that 60 percent of the total amount of blood in the left ventricle is pushed out with each heartbeat. A normal heart’s ejection fraction is between 55 and 70 percent.We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.
For example, if 60% of the blood in the ventricle is pushed out, then the EF is expressed as either 60% or written as a decimal—0.6. . it is the ejection fraction of the left ventricle—often referred to as LVEF (left . There is growing evidence that patients with severe aortic stenosis and LVEF 50-60% have a higher rate of adverse outcomes compared to patients with LVEF >60%. A meta-analysis suggests that impaired LV GLS despite LVEF >50% is associated with reduced survival. After the publication of the treatment arm of SOLVD (Studies of Left Ventricular Dysfunction) in 1991, left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) has been used to define the indication for various drug and device treatments for .
The LVEF can show the extent of damage from a heart attack, long-term high blood pressure, left-sided heart failure, or chemotherapy. Right Ventricular Ejection Fraction (RVEF) Die Bestimmung linksventrikuläre Ejektionsfraktion (LVEF) erfolgt über die Messung des Herzvolumen zu bestimmten Phasen der Herzaktion. . Der Normwert für die linksventrikuläre Ejektionsfraktion beträgt in Ruhe 55-65%. Unter maximaler Belastung steigt dieser Wert bis auf 75% an. Das bedeutet, dass Ihr Herz sich nie „leer pumpt“ und .An ejection fraction (EF) is the volumetric fraction (or portion of the total) of fluid (usually blood) ejected from a chamber (usually the heart) with each contraction (or heartbeat).It can refer to the cardiac atrium, [1] ventricle, [2] gall bladder, [3] or leg veins, [4] although if unspecified it usually refers to the left ventricle of the heart. EF is widely used as a measure of the .
Contrary to the LVEF cutoffs used to define HFpEF in current heart failure guidelines, recent epidemiologic data suggest that mortality risk shows a U-shaped relationship for LVEF with a nadir of risk at an LVEF of 60% to 65% in routine clinical practice, 12 further supporting the differences in HFpEF phenotypes according to the ranges of LVEF.The principal findings were as follows: (1) the higher the pre-LVEF was, the greater was the decrease in LVEF immediately after MVr; (2) the long-term post-LVEF reached a plateau of approximately 60% when the pre-LVEF was ≥50%, but seemed to show a downward trend after reaching a peak at approximately 3–4 years after MVr when the pre-LVEF .
50% to 60% for year five. 30% for 10 years. A different study found that people who had heart failure had expected life spans ranging from three to 20 years after their hospital stay, depending on various factors like age and assigned sex at birth. It’s important to look at your specific situation when considering your prognosis.
what does 60% mean
hermes shop2shop paket
versace condoms
hermes taschen outlet
lvef spect nuclear stress viability
It’s important to note though: this style is not to be confused with the Reissue 2.55 (which looks similar). Reissue bags were introduced under Karl Lagerfeld in 2005 to celebrate the 2.55 style’s 50th birthday. Today, the term Reissue refers to the newer produced 2.55 bags. Shop All Reissue.
lvef 60-65|borderline left ventricular ejection fraction