normal lvef range The ejection fraction (EF) formula equals the amount of blood pumped out of the ventricle with each contraction (stroke volume or SV) divided by the end-diastolic volume (EDV), the total amount of blood in the ventricle. To express as a percentage, you would multiply by . See more Whether you want cheap breakfast buffets in Las Vegas, or fancy a la carte brunches in Vegas, these are the top places to try out. 1. Mr. Mamas Breakfast & Lunch. Located away from the dazzling lights of the Vegas strip and in an unassuming street mall, Mr. Mamas serves a Vegas breakfast menu as large as the number of 5-star ratings .
0 · what is a normal ejection fraction with age
1 · what is a dangerously low ejection fraction
2 · normal ejection fraction by age chart
3 · lvef normal range and echocardiogram
4 · lv systolic function normal range
5 · left ventricular ejection fraction by age
6 · ejection fraction heart failure chart
7 · 30 ejection fraction prognosis
Pokemon Charizard G LV.65 20/147. This is Charizard G LV.65 from Platinum Supreme Victors set from back in 2009. Graded 9 by PSA the card is in mint condition. Stunning card for any Pokemon collector. Will come shipped with lots of protection. Any questions, or if you want more pics, just ask. Thanks! Terms. Payments. Shipping/Returns. Terms.
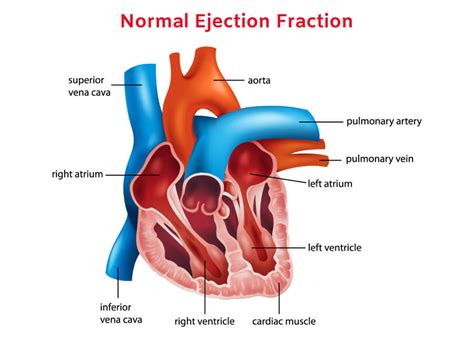
Ejection fraction refers to how well your heart pumps blood. It is the amount of blood pumped out of your heart’s lower chambers (ventricles) each time it contracts. To understand ejection fraction, it’s helpful to understand how blood flows through the heart: 1. Blood enters the heart through the top right section . See moreEjection fraction in a healthy heart is 50% to 70%. With each heartbeat, 50% to 70% of the blood in your left ventricle gets pumped out to your body. Some people with a normal ejection fraction also have heart failure. This is known as heart failure with preserved . See moreThe lower the ejection fraction, the weaker your heart’s pumping action is. This occurs in people with severe heart failure. You can also have a low . See moreThe ejection fraction (EF) formula equals the amount of blood pumped out of the ventricle with each contraction (stroke volume or SV) divided by the end-diastolic volume (EDV), the total amount of blood in the ventricle. To express as a percentage, you would multiply by . See more
With preserved ejection fraction (diastolic heart failure), contractions pump a large portion of blood out to your body. But the left ventricle holds a . See more Ejection fraction (EF) is a percentage of how much blood the left ventricle pumps out with each contraction. A normal EF is between 55 and 70 percent, but it can vary .
A left ventricle (LV) ejection fraction of about 50% to 70% is categorized as normal. A mildly reduced LV ejection fraction is usually between 41% and 49%. A reduced LV . Normal ranges for two-dimensional echocardiography obtained LVEF as per the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging are: LVEF (%) among the male .
gucci shoes women replica
Thus, there is no clear range at which we can say the LVEF is normal (optimal health). For those enrolled in clinical trials (those without severe systemic disease), it appears that the higher the LVEF, the better the outcome. Many doctors consider a normal ejection fraction to be 55%-75%. If yours is 50% or lower, it's a sign that your heart--usually your left ventricle--may not pump out enough blood. There's a gray. A normal LVEF range varies by race, sex, and clinical characteristics, and is associated with different outcomes in heart failure. Learn how to interpret LVEF thresholds . Ejection fraction is measured as a percentage of the total amount of blood in your heart that is pumped out with each heartbeat. A normal ejection fraction is 50 percent or higher. An ejection fraction below 40 percent means .
The British Society of Echocardiography recently updated their normal reference intervals for assessment of cardiac dimensions and function. 1 They describe four categories of left ventricular function and a ‘normal’ LVEF is defined as ≥55%.What Is a Normal Ejection Fraction by Age ? Even a healthy heart doesn’t pump all the blood from the left ventricle in a single cycle. Therefore, an ejection fraction of 55 to 65% is considered normal. – Normal Ejection Fraction by Age – 55 to . a depressed LVEF to persuade patients of the need for treatment. Therefore, patients often use any change in LVEF to track progress or deterioration in their condition. Although misguided, many patients will assume a report indicating a normal LVEF indicates recovery. Article, see p 732 The best method to define a normal LVEF, or anyLVEF = LVEDV – LVESV / LVEDV Normal Ranges for LV Size and Function Normal values for LV chamber dimensions (linear), volumes and ejection fraction vary by gender. A normal ejection fraction is 53-73% (52-72% for men, 54-74% for women).
normal or preserved LVEF [≥50%] (HFpEF) moderately reduced LVEF [in the range of 41–49%] (HFmrEF) reduced LVEF [≤40%] (HFrEF)] A chronically low ejection fraction less than 30% is an important threshold in qualification for disability benefits in the US. [22] Calculation
LVEF should be derived from 2D volume data using the biplane Simpson’s method. Normal LVEF is defined as an EF ≥55%. Patients with an LVEF between 50 and 54% are defined as having ‘borderline low LVEF’. Patients with an LVEF between 36 and 49% are defined as having ‘impaired LVEF’.
The ejection fraction (EF) is the amount of blood your heart pumps (or ejects) with each heartbeat and is a useful way of measuring LVSD. A normal EF is about 55-65 per cent. It’s important to understand that “normal” is not 100 per cent. Measuring the EF helps your doctor to understand how well the heart is pumping. First, the extended LVEF range covered by “mildly reduced” (<55%) means a larger proportion of patients potentially qualifying for proven treatments currently limited to HF with more severely reduced LVEF. . Echocardiographic Normal Ranges Meta-Analysis of the Left Heart Collaboration. "Ethnic-specific normative reference values for . 55 to 70% – Normal heart function. 40 to 55% – Below normal heart function. Can indicate previous heart damage from heart attack or cardiomyopathy. Higher than 75% – Can indicate a heart condition like hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, a common cause of sudden cardiac arrest. Less than 40% – May confirm the diagnosis of heart failure.However, with the “normal” classification for LVEF being set at 55% to 65% and an increased risk for HF associated with an LVEF of <50%, this raises the question as to whether there is any increased risk among patients that fall in the 50% to 55% range.
A normal heart’s ejection fraction is between 55 and 70 percent. . In this case, your heart might still have an ejection fraction that falls in the normal range because your heart is pumping out a normal percentage of the blood that enters it. However in HFpEF, the total amount of blood pumped isn’t enough to meet your body’s needs. .
Normal ejection fraction (50% to 70%): Your heart is getting the job done! Mildly below normal (41% to 49%): Though you may not have symptoms, your heart has started to struggle to pump enough . An LVEF of 50% or more is considered normal. If a person has symptoms of heart failure with a normal ejection fraction, this is referred to as heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), formerly known as diastolic heart failure .We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.
Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is a surrogate for left ventricular global systolic function, defined as the left ventricular stroke volume divided by the end-diastolic volume. . (normal range 35-65%) the endocardium is traced at end-systole and end-diastole in the parasternal short-axis at the mid-papillary level; FAC = (LV end .
Normal values for LVEF, EDV, ESV, and stroke volume are shown in Table 1. . View in full-text. Similar publications +3. How to Perform Parathyroid 4D CT: Tips and Traps for Technique and . A normal ejection fraction ranges from 50% to 70%. Ejection fraction (EF) describes how well your heart chambers (the left or right ventricles) can pump blood to your body to deliver oxygen and nutrients. . (LVEF) below normal. certain children 1 year of age and older with heart failure that causes symptoms. Entresto is a combination of two .
Several studies have defined CMR normal ranges of LV volumes and function in limited age ranges [2–8], and none of these have examined these parameters over a wide age range in healthy individuals. A recent study . classifications of heart failure using LVEF. Heart failure definition. Heart Failure with. Reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) - LVEF<40%; Mid-range ejection fraction (HFmEF) - LVEF 40- 49%; Preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) - LVEF>=50%; Heart failure definition. Systolic impairment and EF. Severe reduction - EF <35%; Moderate reduction - EF 35-39%The response of LVEF to vasodilator stress, a potential marker of disease severity, was relatively similar among the software (Fig. 2). Comparison of Subgroups of Healthy Subjects The mean values of normal LVEF in patients with a low pretest probability of CAD (subgroup 1) and normal coronary CTA findings (subgroup 2) are depicted in Figures
According to the definition in European and US guidelines, the normal EF range is 52–72% in men and 54–74% in women, with normal values plus or minus standard deviation being 62 ± 5% for men .
Published normal ranges for LVEF have varied between techniques. Myocardial strain is a dimensionless variable representing the change in length between two points over the cardiac cycle, and can be quantified using echocardiography or CMR tissue tracking. Regional strain is less reproducible; whereas peak global strain is more consistent .
Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction (LVEF) Definition. Ejection Fraction (EF) is a percentage of blood pumped by the LV with each contraction. Many factors can affect ejection fraction including preload, afterload, and contractility. A normal EF ranges from 55-69%, and is calculated using the following equation:
Cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) enables assessment and quantification of morphological and functional parameters of the heart, including chamber size and function, diameters of the aorta and pulmonary arteries, flow and myocardial relaxation times. Knowledge of reference ranges (“normal values”) for quantitative CMR is crucial to .We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is the percentage of oxygen-rich blood pumped out from the left ventricle into the arteries that carry blood to vital organs, muscles, and tissues. . LVEF; lvef full form; lvef normal range by age; right ventricular ejection fraction; symptoms of low ejection fraction; symptoms of low lvef; Systolic .
‘What is a normal left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF)?’ A simple question that one would assume has a straightforward answer given that LVEF is one of the most frequently applied metrics in cardiology for diagnosis, risk stratification and management of multiple conditions, ranging from hypertension and coronary artery disease to heart failure (HF). The simple .Weighted mean normal values for LVEF at rest were 62.3 +/- 6.1% (ISD) with a lower limit of normal of 50% and for RVEF 52.3 +/- 6.2% (N = 365) with a lower limit of normal of 40%. During exercise, LVEF increased in 475 subjects by +8.0 EF% (range 3-15%), a normal increase being accepted to be greater than or equal to 5% over a normal resting .
what is a normal ejection fraction with age

Get the best deals on Louis Vuitton Messenger Bags when you shop the largest online selection at eBay.com. Free shipping on many items | Browse your favorite brands | affordable prices.
normal lvef range|lv systolic function normal range